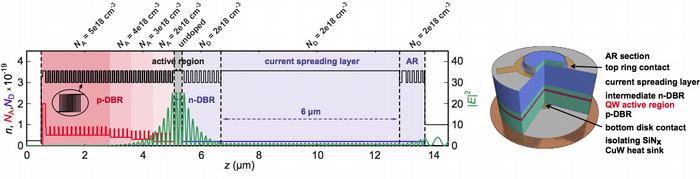
Electrically pumped VECSELs and MIXSELs
Besides the MIXSEL approach, we are also working on a second approach to reduce size and cost of SESAM-modelocked VECSELs. Since VECSELs are semiconductor-based, pumping them electrically is an obvious next step towards more compact, cost-efficient ultrafast laser sources suitable for mass production.
The design of an electrically pumped VECSEL (EP-VECSEL) requires a certain tradeoff between optical and electrical properties Download Ref. [268] (PDF, 702 KB). This is due to the fact that the device must be doped to enable efficient electrical conductivity, whereas the free carrier absorption related with doping compromises the optical performance.
In our first realization of an EP-VECSEL, MBE-grown and processed in the FIRST cleanroom facility at ETH Zürich, we have demonstrated output powers of up to 120 mW in continuous-wave (cw) operation Download Ref. [321] (PDF, 667 KB).
In 2012, we presented a detailed gain characterization of EP-VECSELs in collaboration with Philips. There we were able to show that an optimized EP-VECSEL gain chip is suitable for ultrashort pulse generation. 9.5-ps pulses with an average output power of 7.6 mW and a repetition rate of 1.4 GHz were obtained Download Ref. [337] (PDF, 1.3 MB).
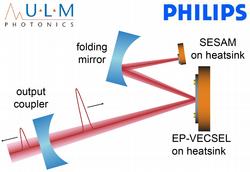
Improving the beam quality, the electrical resistance and the thermal management of our own EP-VECSELs, we achieved up to 170 mW in cw operation. Passively modelocking our devices we obtained 7.3-ps pulses with an average output power of 13.1 mW at a repetition rate of 1.5 GHz and even pulses as short as 6.3 ps Download Ref. [350] (PDF, 636 KB). These are the shortest pulses from a modelocked EP-VECSEL to date.
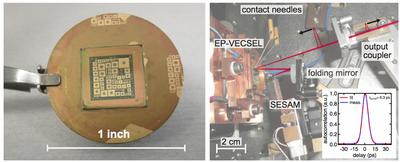
The next steps in our ongoing work are the improvement of the single-mode performance of our EP-VECSELs to increase the average output power in modelocked operation and subsequently the development of the absorber integration into the EP-VECSEL. An electrically pumped MIXSEL would be a breakthrough achievement for the mass production of ultrafast, compact laser sources.
References
[268] P. Kreuter, B. Witzigmann, D. J. H. C. Maas, Y. Barbarin, T. Südmeyer and U. Keller
Download “On the design of electrically pumped vertical-external-cavity surface-emitting lasers” (PDF, 702 KB)
Appl. Phys. B, vol. 91, 257-264, 2008
[321] Y. Barbarin, M. Hoffmann, W. P. Pallmann, I. Dahhan, P. Kreuter, M. Miller, J. Baier, H. Moench, M. Golling, T. Südmeyer, B. Witzigmann, U. Keller
Download “Electrically pumped vertical external cavity surface emitting lasers suitable for passive modelocking” (PDF, 667 KB)
IEEE J. Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics (JSTQE), vol. 17, No. 6, pp. 1779-1786, 2011
[337] W. P. Pallmann, C. A. Zaugg, M. Mangold, V. J. Wittwer, H. Moench, S. Gronenborn, M. Miller, B. W. Tilma, T. Südmeyer, U. Keller
Download “Gain characterization and passive modelocking of electrically pumped VECSELs” (PDF, 1.3 MB)
Optics Express, vol. 20, pp. 24791-24802, 2012
[350] W. P. Pallmann, C. A. Zaugg, M. Mangold, I. Dahhan, M. Golling, B. W. Tilma, B. Witzigmann, U. Keller
Download “Ultrafast electrically pumped VECSELs” (PDF, 636 KB)
IEEE Photonics Journal, vol. 5, Nr. 4, 1501207, 2013
[368] C. A. Zaugg, S. Gronenborn, H. Moench, M. Mangold, M. Miller, U. Weichmann, W. P. Pallmann, M. Golling, B. W. Tilma, U. Keller,
Download “Absorber and gain chip optimization to improve performance from a passively modelocked electrically pumped vertical external cavity surface emitting laser” (PDF, 635 KB)
Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 104, 121115, 2014