Ultrafast thin disk laser
Thin disk laser basics
The thin disk laser (TDL) was invented by A. Giesen and co-workers, in Stuttgart, Germany:
A. Giesen, H. Hügel, A. Voss, K. Wittig, U. Brauch, H. Opower
external page "Scalable concept for diode-pumped high-power solid-state lasers"
Appl. Phys. B 58, 365-372 (1994).
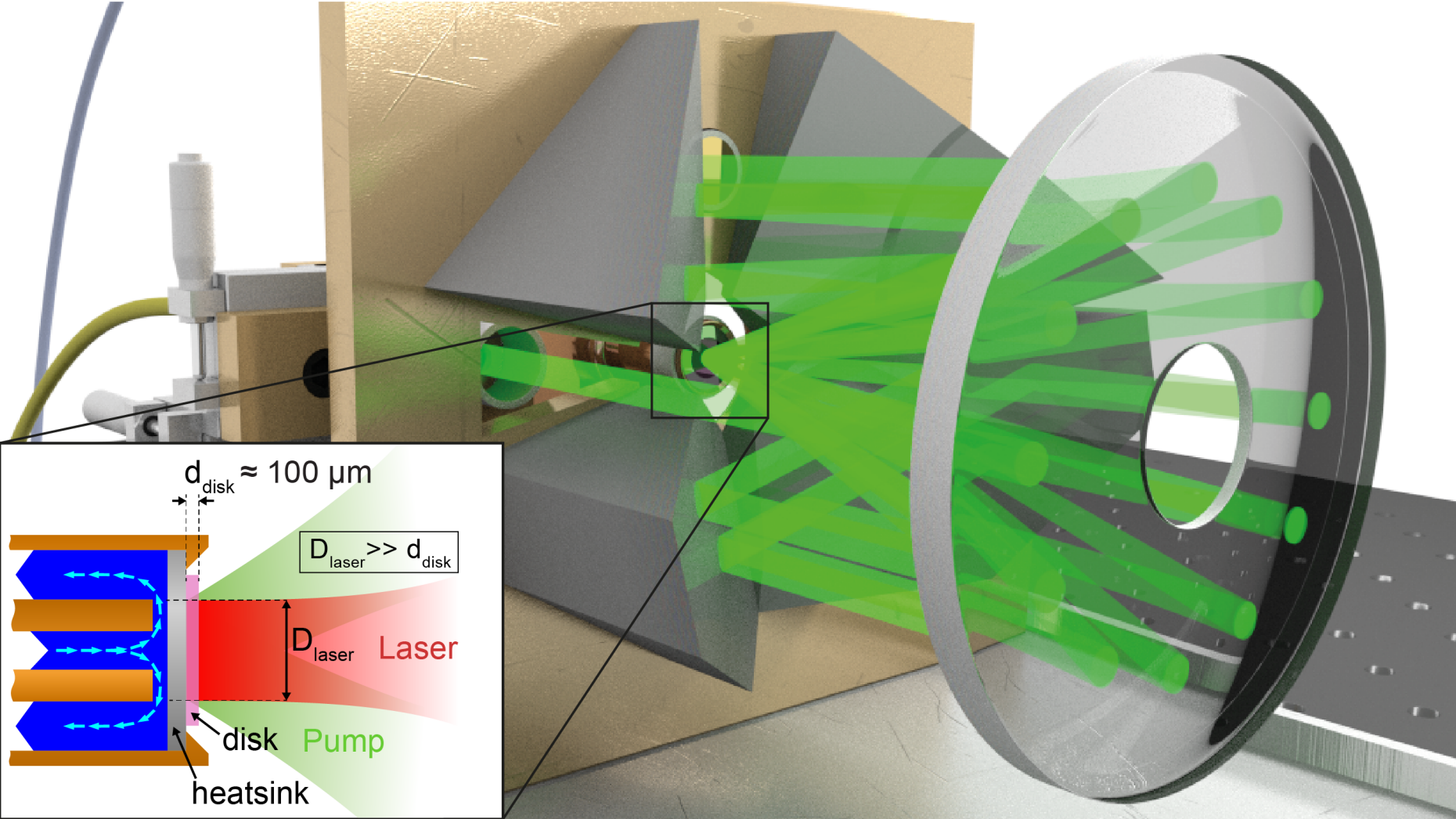
A TDL is a diode-pumped solid-state laser with a gain crystal that has the shape of a thin disk and is used in reflection (as an "active mirror") in a resonator. Typically, the disk has a thickness of few hundred micrometers, whereas laser spot sizes can reach several millimeters. For an efficient heat removal, the backside of the disk is mounted on a heat sink (typically copper or diamond) that is water-cooled. The resulting 1D heat-flow results in straightforward power scalability.
Multiple passes of the pump light over the disk guarantee an efficient absorption of the pump light. Commercially available pump-pass cavities generate > 24 pump passes through the disk to ensure efficient absorption.
A good gain material for TDLs combines good thermal conductivity, a large absorption cross-section at high doping levels and high emission cross section. In addition, for ultrafast applications, a broad emission bandwidth that supports the generation of ultrashort pulse durations is crucial.The most widely-used gain material for TDLs is Yb:YAG, which can be grown in excellent quality and with large diameters. However, other materials have recently attracted a lot of attention for this geometry, which exhibit much broader emission spectra than Yb:YAG (see section on pulse duration scaling for more details).
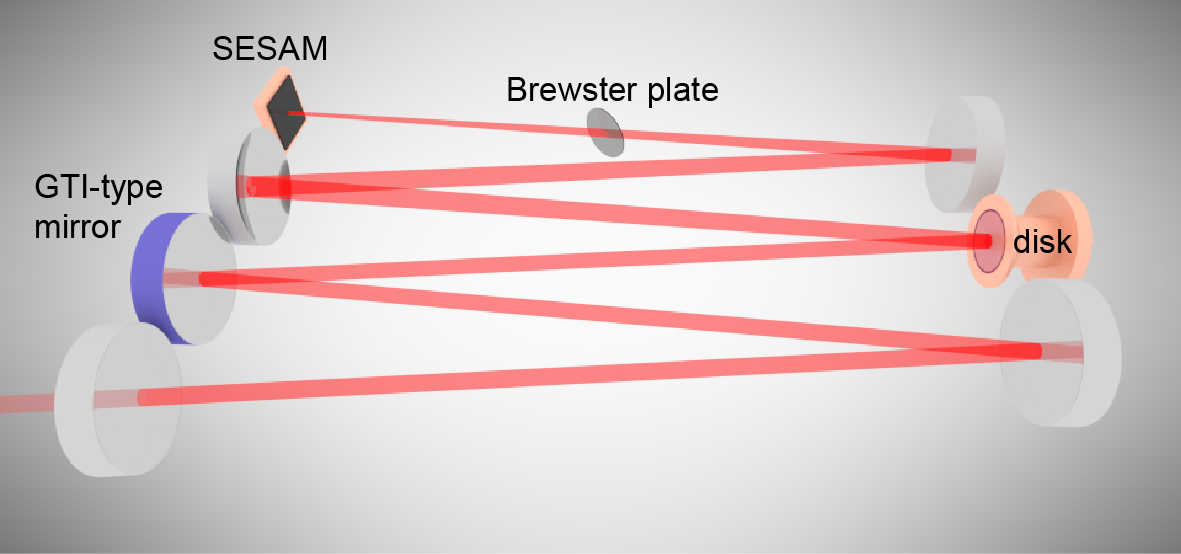
SESAM modelocking of thin-disk lasers
We focus our efforts on modelocking of high-power TDLs using Semiconductor Saturable Absorber Mirrors (SESAMs). SESAMs were invented by Prof. Keller in 1992:
Download "Solid-state low-loss intracavity saturable absorber for Nd:YLF lasers: an antiresonant semiconductor Fabry-Perot saturable absorber" (PDF, 502 KB)
Optics Lett., vol. 17, pp. 505-507, 1992
Download "Semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors (SESAMs) for femtosecond to nanosecond pulse generation in solid-state lasers" (PDF, 394 KB)
IEEE J. Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics (JSTQE), vol. 2, pp. 435-453, 1996
SESAMs are the best suited method to achieve self-starting and robust passive modelocking at extremely high power levels (several kilowatts of average power and peak powers of several hundreds of MW in current record-holding systems).
The basic operation principle of a SESAM is explained in the section about SESAMs. For specific use in TDLs, we design SESAMs with high-damage threshold and special heatsinking to withstand extreme average power and peak power intracavity conditions.
SESAM-modelocked TDLs operate in the soliton modelocking regime. This means a careful balance between nonlinear phase (due to self-phase modulation) and negative group-delay dispersion needs to be achieved within one round-trip of the laser pulses in the laser resonator. For power and energy scaling, careful design guidelines need to be followed to avoid excessive nonlinearities and maintain stable modelocking.
Recent invited review articles:
SESAM modelocked thin disk lasers based on soliton modelocking:
C. J. Saraceno, F. Emaury, C. Schriber, A. Diebold, M. Hoffmann, M. Golling, T. Südmeyer, U. Keller
external page "Toward millijoule level high-power ultrafast oscillators" - Download Download (PDF, 1.3 MB) – Invited Paper
IEEE J. Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics (JSTQE), vol. 1 , No. 1, 1100318, 2015
C. J. Saraceno, C. Schriber, F. Emaury, O. H. Heckl, C. R. E. Baer, M. Hoffmann, K. Beil, C. Kränkel, M. Golling, T. Südmeyer, U. Keller
external page “Cutting-edge high-power ultrafast thin disk oscillators.” - Download Download (PDF, 1.7 MB) - Invited Paper
Appl. Sciences, vol. 3, pp. 355-395, 2013
Laser materials for ultrafast thin disk lasers: Yb-doped sesquioxides
[347] K. Beil, C. J. Saraceno, C. Schriber, F. Emaury, O. H. Heckl, C. R. E. Baer, M. Golling, T. Südmeyer, U. Keller, C. Kränkel, G. Huber
external page "Yb-doped mixed sesquioxides for ultrashort pulse generation in the thin disk laser setup" - Download Download (PDF, 721 KB) Invited Paper
Appl. Phys. B, vol. 113, pp. 13-18, 2013
Modelocking and other tutorials:
Soliton modelocking was first described in:
[63] F. X. Kärtner, I. D. Jung, U. Keller - Invited Paper
Download "Soliton modelocking with saturable absorbers: theory and experiment" (PDF, 515 KB)
IEEE J. Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics (JSTQE), vol. 2, pp. 540-556, 1996
[51] I. D. Jung, F. X. Kärtner, L. R. Brovelli, M. Kamp, and U. Keller
Download "Experimental verification of soliton modelocking using only a slow saturable absorber" (PDF, 334 KB)
Optics Lett., vol. 20, pp. 1892-1894, 1995
More tutorial level of information is also given in this book chapter.
Tutorial lectures with viewgraphs have been published on 2. March 2013 in the News section:
Lecture 1: Download Passive modelocked solid-state lasers (PDF, 12.8 MB)
Lecture 2: Download SESAM (PDF, 18.2 MB)
More info on SESAMs under Research/SESAM.